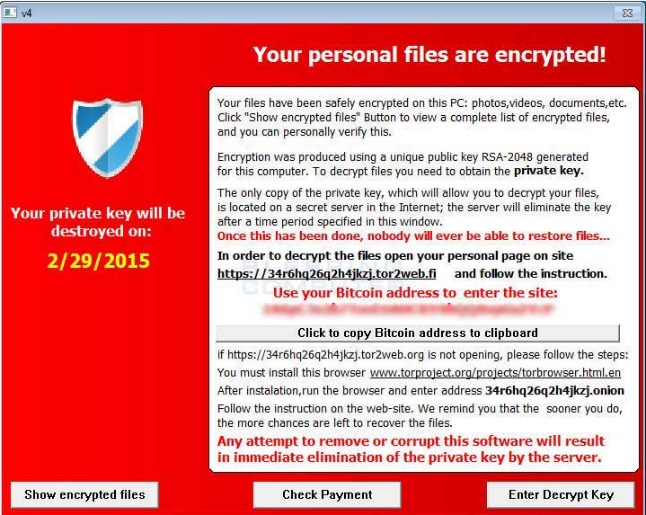
On Friday May 12, 2017 a massive world wide ransomware attack occurred. More than 45,000 incidents affecting 74 countries and counting. Organizations were crippled, including hospitals that had were forced to divert emergencies.
What is Ransomware?
It’s a type of malicious software designed to block access to a computer system files by encrypting them, until a sum of money is paid to unencrypt the files.
Once the files become encrypted, the user cannot access them. Files are still on the system, but not accessible.
Ransomware has some key characteristics that set it apart from another malware:
- It features unbreakable encryption, which means that you can’t decrypt the files on your own.
- It has the ability to encrypt all kinds of files, from documents to pictures, videos, audio files and other things you may have on your computer.
- It can scramble your file names, so you can’t know which data was affected. This is one of the tricks used to confuse and coerce victims into paying the ransom.
- It will add a different extension to your files
- It will display an image or a message that lets you know your data has been encrypted and that you have to pay a specific sum of money to get it back;
- It requests payment in Bitcoins, because this crypto-currency cannot be tracked by cyber security researchers or law enforcements agencies;
- Usually, the ransom payments have a time-limit, to add another level of psychological constraint to this extortion scheme. Going over the deadline typically means that the ransom will increase, but it can also mean that the data will be destroyed and lost forever.
- It uses a complex set of evasion techniques to go undetected by traditional antivirus.
- It often recruits the infected PCs into botnets, so cyber criminals can expand their infrastructure and fuel future attacks;
- It can spread to other PCs connected in a local network, creating further damage;
It frequently features data exfiltration capabilities, which means that ransomware can extract data from the affected computer (usernames, passwords, email addresses, etc.) and send it to a server controlled by cyber criminals; - It sometimes includes geographical targeting, meaning the ransom note is translated into the victim’s language, to increase the chances for the ransom to be paid.
- The inventory of things that ransomware can do keeps growing every day, with each new security alert broadcasted by our team or other malware researchers.
Why Can’t Antivirus Detect Ransomware?
Ransomware uses a complex set of evasion techniques to go undetected by traditional antivirus.
- Communication with Command & Control servers is encrypted and difficult to detect in network traffic;
- It features built-in traffic anonymizers, like TOR and Bitcoin, to avoid tracking by law enforcement agencies and to receive ransom payments;
- It uses anti-sandboxing mechanisms so that antivirus won’t pick it up;
- It employs domain shadowing to conceal exploits and hide the communication between the downloader (payload) and the servers controlled by cyber criminals (where the ransomware is stored);
- It features Fast Flux, another technique used to keep the source of the infection anonymous;
- It deploys encrypted payloads which can make it more difficult for antivirus to see that they include malware, so the infection has more time to unfold;
- It has polymorphic behavior that endows the ransomware with the ability to mutate enough to create a new variant, but not so much as to alter the malware’s function;
- It has the ability to remain dormant – the ransomware can remain inactive on the system until the computer it at its most vulnerable moment and take advantage of that to strike fast and effectively.
How can you recover your files?
The quickest way to recover is to restore your system from a backup. If you do not have a backup, you can attempt to clean or recover manually, with tools that may or may not work depending on the strand of ransomware.
How Can You Prevent a Ransomware Attack?
Ransomware is undetectable by traditional antivirus. You need another layer of IT computer security that can monitor and filter internet activity and block malicious websites. It needs to ensure that your system is not vulnerable with outdated software patches. And since 75% of cyber attacks are brand new and unlisted in antivirus databases, it needs to have the intelligence to block malware that tries to harvest and steal your confidential information.
Find out more by contacting us for a free quote and more information at 416-900-6852 TF 1-877-709-2656 or use our contact form: /contact-us/
Or instant message us by clicking here: https://goo.gl/8dMWyz